In today’s fast-paced world, we often focus on physical health, diet, and exercise as the primary factors influencing our well-being. However, an emerging body of research highlights a surprisingly potent force in determining our health and lifespan—our social connections. The quality and strength of our relationships play a vital role in reducing inflammation, supporting immune function, and ultimately promoting a longer, healthier life.





The Science Behind Social Connections and Health
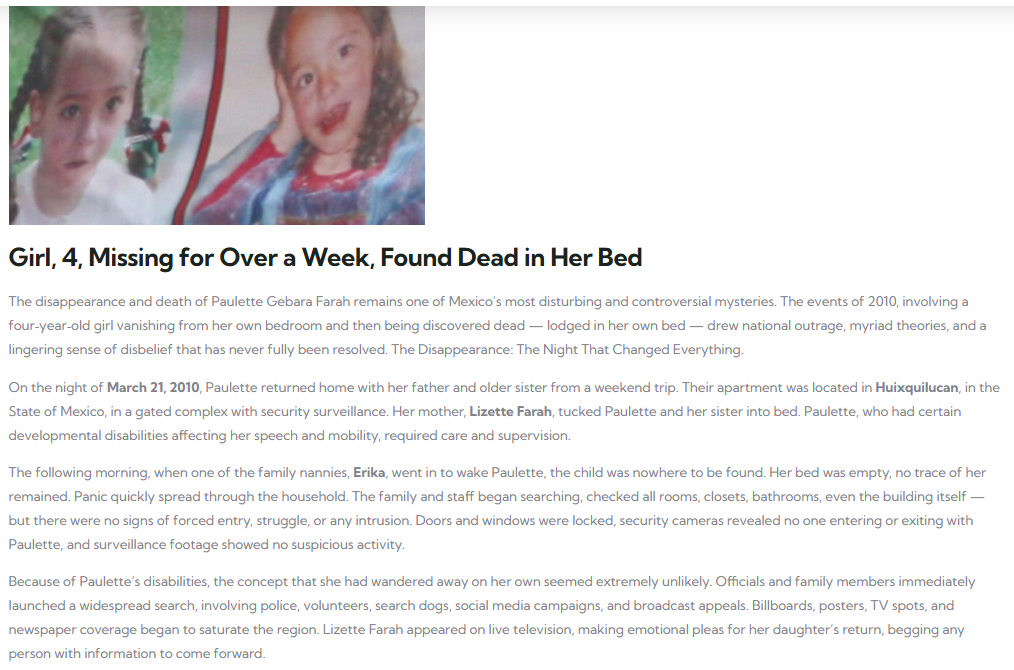
Human beings are inherently social creatures. From early childhood, our survival depended on forming bonds within communities. These connections provided protection, emotional support, and shared resources. Modern science now confirms that these social bonds have a profound biological impact.
Studies have shown that people with strong, supportive relationships tend to have lower levels of chronic inflammation, which is a root cause of many diseases including heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. Inflammation is the body’s natural response to injury or infection, but when it becomes chronic, it contributes to tissue damage and accelerated aging.
How Do Social Bonds Reduce Inflammation?
The link between social relationships and inflammation involves complex biochemical processes. Positive social interactions help regulate the production of stress hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline. When people feel connected and supported, their bodies produce lower levels of these hormones, which in turn reduces the activation of inflammatory pathways.
Moreover, social support promotes healthier lifestyle choices. People embedded in strong social networks are more likely to engage in regular physical activity, maintain balanced diets, and avoid harmful behaviors like smoking or excessive alcohol consumption. These behaviors further help control inflammation.
Emotional Support and Immune System Boost
Emotional support acts as a buffer against the detrimental effects of stress. When individuals face challenges, the presence of empathetic friends or family members can mitigate feelings of anxiety and depression. This emotional comfort translates into physiological benefits: studies reveal improved immune function in people who report feeling emotionally supported.
For example, research indicates that individuals with close social ties have higher counts of protective immune cells such as lymphocytes and natural killer cells. These cells help fight off infections and may even reduce the risk of certain chronic diseases.
Longevity and Social Integration
The benefits of social bonds are not limited to short-term health. Numerous longitudinal studies have demonstrated a strong correlation between social integration and longevity. People with extensive social networks tend to live longer than those who are isolated or lonely.
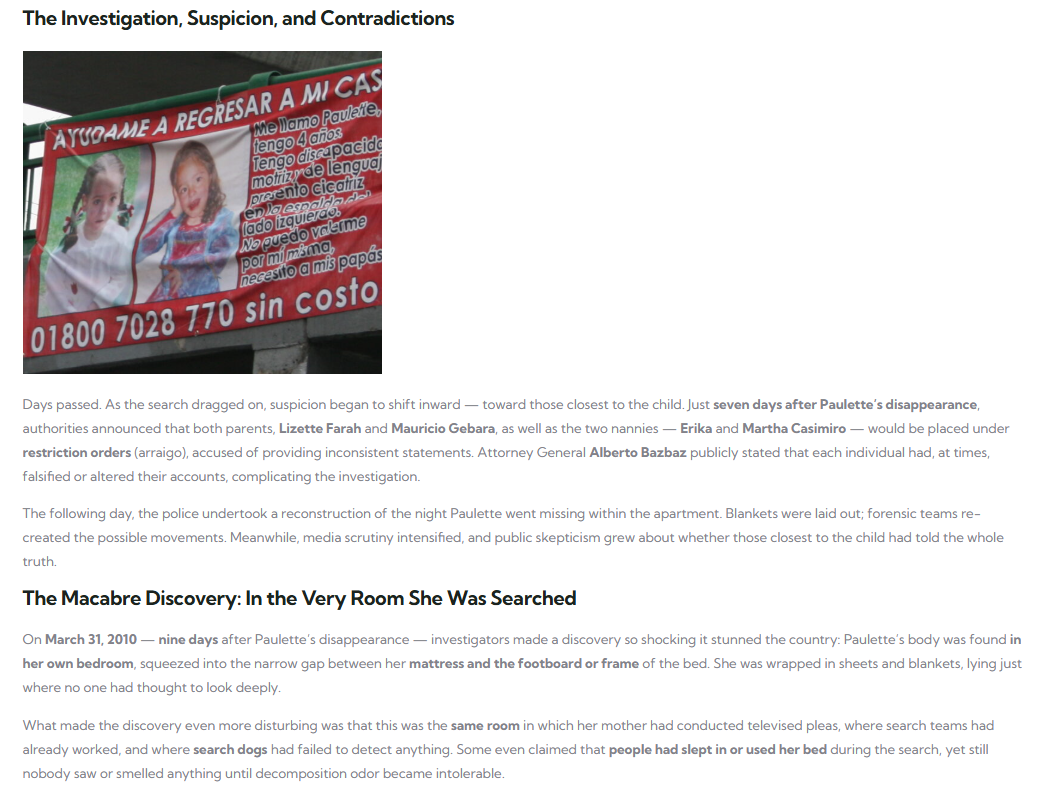
One famous study found that social isolation increases the risk of premature death by nearly 30%. In contrast, individuals with robust social relationships had significantly lower mortality rates, even when controlling for other factors such as socioeconomic status, smoking, and physical health.
Quality Over Quantity: The Importance of Meaningful Connections
It’s important to note that the quality of social interactions matters more than the number of acquaintances. Genuine, supportive relationships provide emotional nourishment and reduce stress, while superficial or strained connections may contribute to tension and increase inflammation.
Healthy relationships foster a sense of belonging, purpose, and self-worth. These psychological benefits are crucial for maintaining mental health, which is closely intertwined with physical health.
Practical Ways to Strengthen Social Bonds
Given the profound health implications, nurturing social connections should be a priority for everyone. Here are some practical steps to build and maintain meaningful relationships:
- Spend Quality Time Together: Engage in activities that allow for deep conversations and shared experiences, such as family dinners, walks, or hobbies.
- Practice Active Listening: Show genuine interest in others’ lives and feelings without judgment.
- Express Gratitude and Appreciation: Acknowledge the positive impact others have on your life.
- Join Community Groups: Participate in clubs, volunteer organizations, or social events to meet like-minded people.
- Maintain Regular Contact: Even brief but consistent interactions, such as phone calls or messages, can strengthen bonds.
Addressing Social Isolation in the Modern Age
Despite the known benefits, social isolation is a growing problem, exacerbated by urbanization, digital distractions, and recent global events like the COVID-19 pandemic. Loneliness can lead to a vicious cycle of withdrawal and increased health risks.
Communities and healthcare systems are now recognizing the need to tackle social isolation as a public health issue. Encouraging social engagement and providing support for vulnerable populations can significantly improve health outcomes.
Conclusion
The connection between social bonds and physical health is undeniable. Strong relationships reduce inflammation, bolster the immune system, and contribute to a longer, more fulfilling life. In essence, investing in social connections is an investment in our health and longevity.
While medical advancements continue to improve treatment options, the simple act of nurturing meaningful relationships remains one of the most powerful tools for enhancing well-being. By prioritizing social bonds, individuals can enjoy not only emotional satisfaction but also tangible health benefits that support a vibrant, extended lifespan.



