Body Mass Index (BMI) Calculator – Detailed Guide
The Body Mass Index (BMI) Calculator helps estimate whether your current weight is within a healthy range for your height. By using your height and weight, the calculator provides a BMI value along with a weight category such as underweight, normal, overweight, or obese.
In addition to BMI, this calculator also displays the Ponderal Index (PI), which can be more informative for individuals who are very tall or very short. All results are calculated automatically based on the values you enter.
What Is BMI?
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a numerical value that represents the relationship between a person’s height and weight. It is commonly used worldwide as a screening tool to assess whether a person may be underweight, at a healthy weight, overweight, or obese.
BMI does not directly measure body fat, but it is widely accepted as a simple and useful indicator for identifying potential weight-related health risks.
Why BMI Is Used
- Easy to calculate
- Useful for large populations
- Helps identify possible health concerns
- Recommended by organizations such as WHO and CDC
BMI Categories for Adults (Age 20+)
The following BMI ranges are based on international health standards and apply to both men and women aged 20 years or older.
| Classification | BMI Range (kg/m²) |
|---|---|
| Severe Thinness | Below 16 |
| Moderate Thinness | 16 – 17 |
| Mild Thinness | 17 – 18.5 |
| Normal Weight | 18.5 – 25 |
| Overweight | 25 – 30 |
| Obese Class I | 30 – 35 |
| Obese Class II | 35 – 40 |
| Obese Class III | Above 40 |


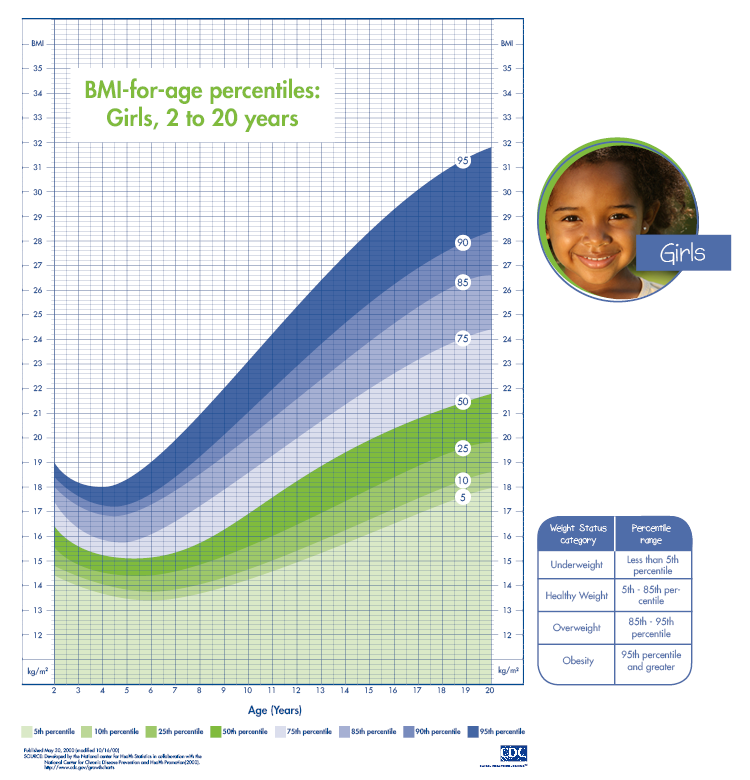
BMI for Children and Teenagers (Age 2–20)
For children and teenagers, BMI is interpreted differently. Instead of fixed ranges, BMI is compared against age- and gender-specific percentiles.
| Category | Percentile Range |
|---|---|
| Underweight | Below 5% |
| Healthy Weight | 5% – 85% |
| At Risk of Overweight | 85% – 95% |
| Overweight | Above 95% |
Separate growth charts are used for boys and girls to ensure accurate assessment.


Health Risks of Being Overweight
Having a BMI in the overweight or obese range may increase the risk of several health conditions, including:
- High blood pressure
- Unhealthy cholesterol levels
- Type 2 diabetes
- Heart disease and stroke
- Joint problems such as osteoarthritis
- Breathing issues, including sleep apnea
- Certain cancers
- Reduced quality of life and mobility
Maintaining a healthy BMI can significantly reduce these risks. Individuals with higher BMI values are advised to consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
Health Risks of Being Underweight
Being underweight can also lead to health concerns, such as:
- Nutrient deficiencies and anemia
- Weak bones and increased fracture risk
- Lower immune system strength
- Growth and development issues (in children and teens)
- Hormonal imbalances and fertility issues
- Higher risk during medical procedures
Unexplained or persistent low body weight should be evaluated by a medical professional.
Limitations of BMI
While BMI is a helpful screening tool, it has limitations and should not be used alone to judge health.
Important Considerations
- BMI does not distinguish between muscle and fat
- Athletes may have high BMI due to muscle mass
- Older adults may have more body fat at the same BMI
- Men and women store fat differently
- Ethnicity and genetics also influence body composition
Because of these factors, BMI should be considered alongside other measurements and lifestyle factors.



BMI Formula Explained
Metric Units (SI)
BMI = weight (kg) ÷ height² (m²)US Units
BMI = 703 × weight (lb) ÷ height² (in²)Both formulas produce the same BMI value when calculated correctly.
What Is BMI Prime?
BMI Prime is a ratio that compares your BMI to the upper limit of the normal BMI range (25 kg/m²).
BMI Prime = BMI ÷ 25BMI Prime Interpretation
| Classification | BMI Prime |
|---|---|
| Underweight | Below 0.74 |
| Normal | 0.74 – 1.00 |
| Overweight | 1.00 – 1.20 |
| Obese | Above 1.20 |
BMI Prime allows quick comparison across populations and helps show how far a BMI value is from the healthy upper limit.
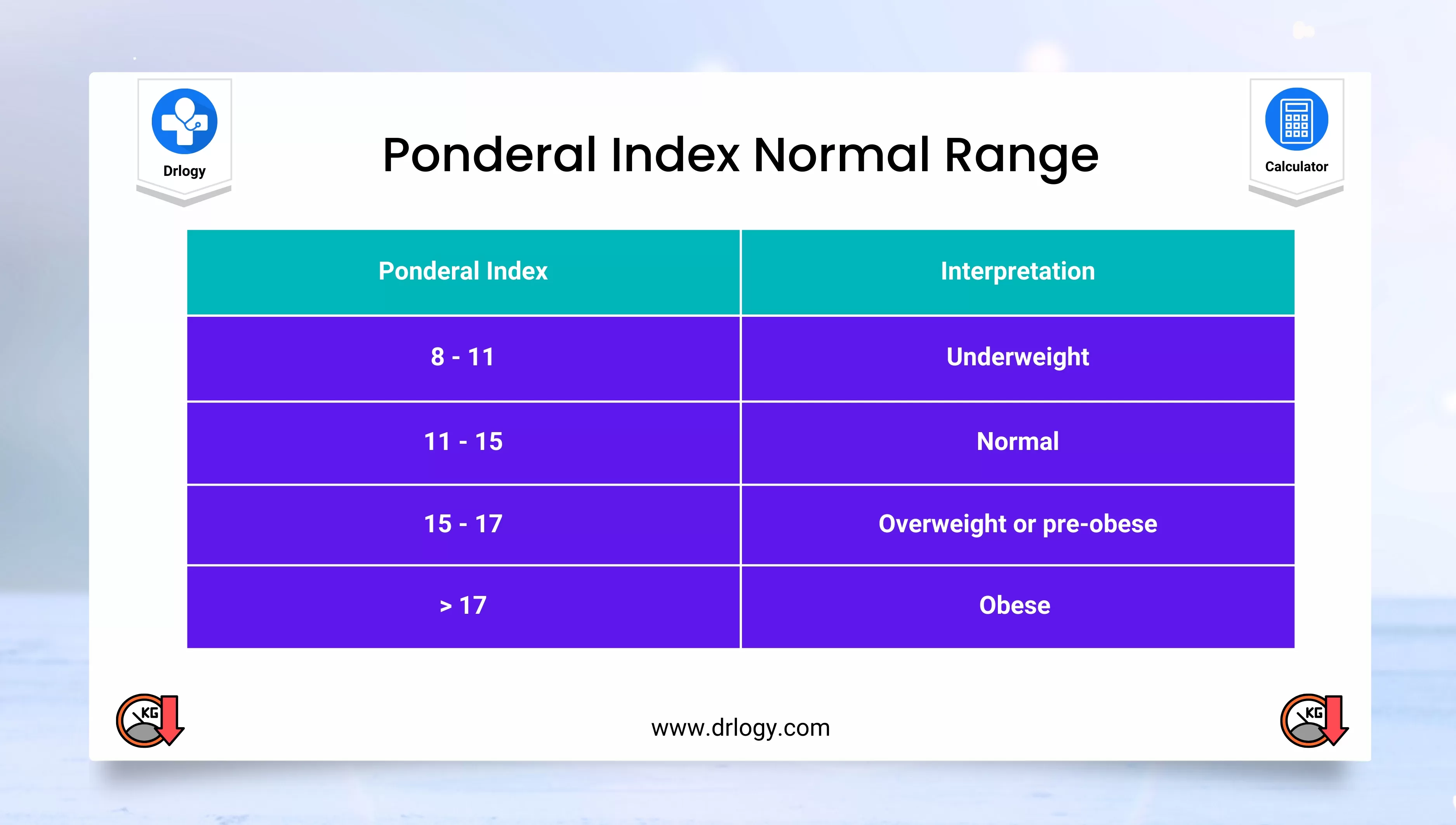
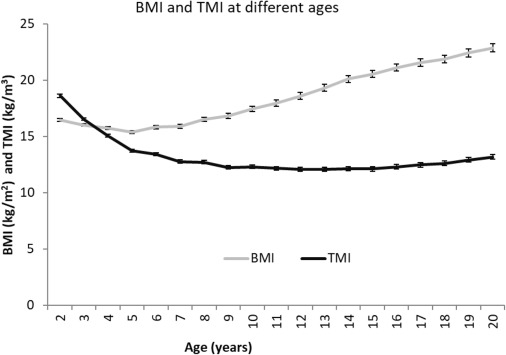
What Is the Ponderal Index?
The Ponderal Index (PI) is similar to BMI but uses height cubed instead of squared. This makes it more suitable for people at extreme heights.
Metric Formula
PI = weight (kg) ÷ height³ (m³)Why Ponderal Index Matters
- More accurate for very tall or very short individuals
- Reduces BMI distortion at height extremes
- Useful as a secondary measurement

Final Note
BMI, BMI Prime, and the Ponderal Index are informational tools, not diagnostic tests. They are most effective when used as part of a broader health assessment that includes diet, physical activity, and professional medical advice.
Using this calculator regularly can help you track trends, understand your body better, and make informed lifestyle choices.
