Have you ever noticed how your eyes feel dry or strained after a long day of staring at a screen? Or how you tend to blink less when you’re fully engrossed in work, and more frequently when you’re zoning out? These subtle shifts in your eye blinking rate aren’t just quirks—they can actually reveal a lot about your mental fatigue levels.

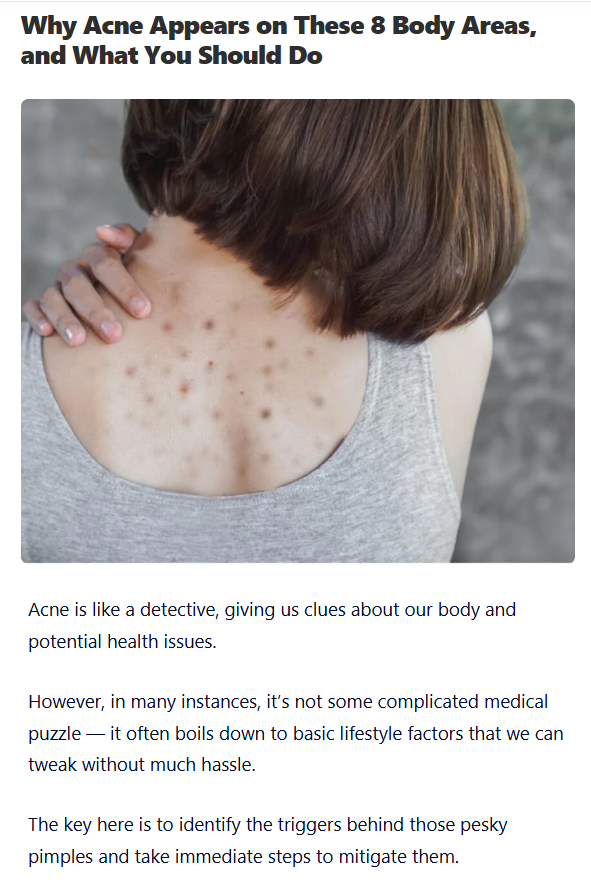
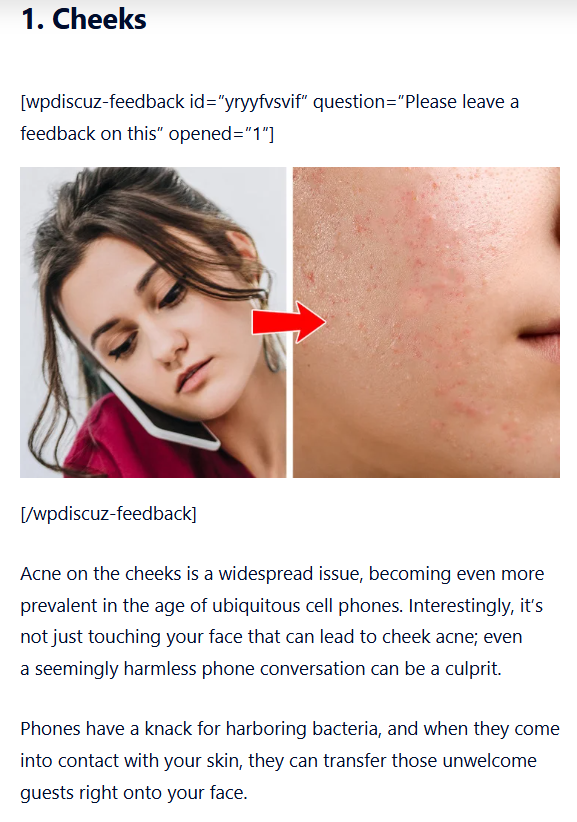
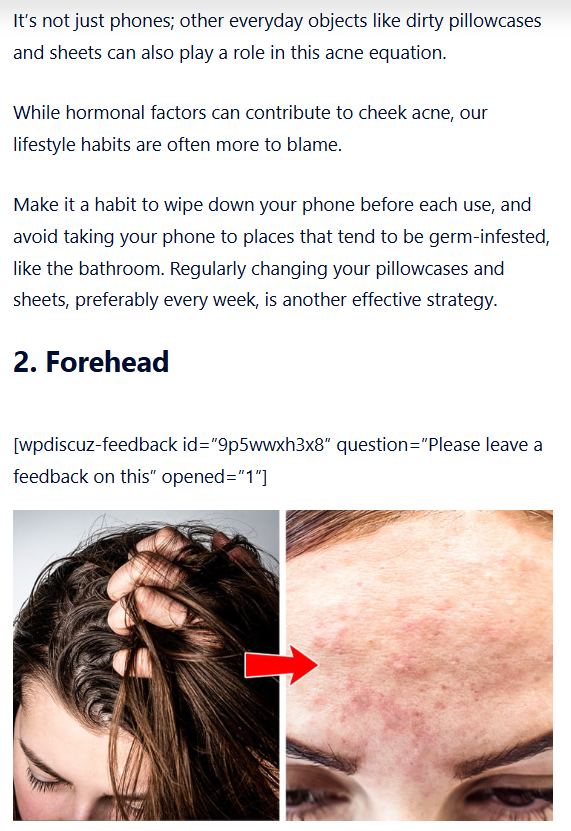

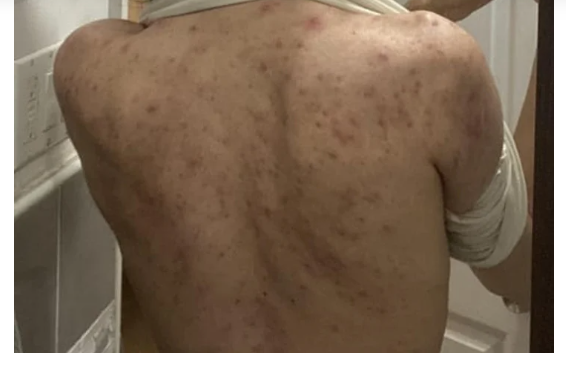





Blinking may seem like a simple reflex, but it’s tightly linked to both cognitive function and neural activity. Researchers have found that changes in blink frequency can signal when your brain is running low on energy, when your attention is slipping, or when your body is nudging you to take a break.
In this article, we’ll explore how blinking functions as a biological indicator of mental exhaustion, the science behind it, and how you can use this knowledge to better manage focus, productivity, and overall brain health.
The Biology of Blinking
Blinking serves several essential purposes: it lubricates the eyes, clears debris, and protects your vision. On average, a person blinks 15 to 20 times per minute during relaxed activities. However, that number can change dramatically depending on what you’re doing—and how mentally taxed you are.
Blink rate is controlled by both involuntary reflexes and central nervous system regulation, which is why it becomes a useful marker for neurological and emotional states. When you’re stressed, tired, or deeply focused, your blinking behavior changes without you even realizing it.
Mental Fatigue: What Happens in the Brain
Mental fatigue occurs when the brain has been working hard for an extended period—whether you’re crunching numbers, studying for hours, or engaging in emotionally draining conversations. It’s characterized by:
- Reduced concentration
- Slower reaction times
- Memory lapses
- Decreased motivation
- Feeling mentally “foggy” or irritable
At the neurological level, prolonged mental activity increases adenosine accumulation in the brain and reduces neurotransmitters that support alertness and executive function. As mental fatigue builds, the brain starts showing signs of decreased efficiency—and your blink rate often reflects that shift.
The Blink-Fatigue Relationship: What Science Says
Several studies have explored the connection between blink rate and mental fatigue, particularly in fields like aviation, neurology, and occupational health.
🔹 Lower Blink Rate During High Focus
During intense concentration (e.g., reading, programming, gaming), people tend to blink significantly less. In fact, studies show blink rates can drop to as low as 3–8 blinks per minute during high-focus tasks. This reduction helps maintain visual stability—but it also contributes to eye strain and dryness.
🔹 Higher Blink Rate with Mental Exhaustion
As mental fatigue sets in, blink rates tend to increase. This is the brain’s way of signaling declining alertness and processing capacity. An uptick in blinking often coincides with:
- Decreased task performance
- Difficulty maintaining attention
- Increased error rates
- Subjective reports of tiredness
This natural increase in blinking is thought to be a neurological cue that your brain needs rest or a cognitive reset.
Blinking and the Dopamine Connection
Interestingly, blinking isn’t just about eye protection—it’s also linked to dopamine levels in the brain. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter involved in motivation, learning, and focus. Several studies suggest that baseline blink rate correlates with dopamine activity.
- Higher dopamine = more frequent blinking
- Lower dopamine = slower blink rate
When mental fatigue causes dopamine levels to drop, the brain responds by adjusting blink rate. This makes blinking not only a physical indicator of eye fatigue but also a marker of neurochemical changes associated with cognitive exhaustion.
Visual Fatigue vs. Mental Fatigue: Are They the Same?
While visual fatigue (tired or strained eyes) and mental fatigue often go hand-in-hand, they’re not identical. Visual fatigue comes from prolonged use of the eyes—especially screen time—whereas mental fatigue is broader, encompassing emotional and cognitive stress.
However, both types of fatigue can:
- Disrupt natural blinking rhythms
- Trigger increased blinking frequency
- Lead to headaches, reduced focus, and irritability
- Impact task performance and emotional resilience
Because blinking is influenced by both visual and cognitive load, it’s a valuable early warning system for when you need a break.
Using Blink Rate as a Personal Fatigue Gauge
Tracking your blink rate doesn’t require specialized tools—just some self-awareness and observation. Here are a few signs that your blinking pattern is trying to tell you something:
🟠 Fewer blinks than normal?
You’re likely in a high concentration zone, which might mean you’re being productive—but it also means you’re at risk of visual fatigue. Try the 20-20-20 rule (every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds) to give your eyes a reset.
🔵 More blinks per minute than usual?
This could be a sign that mental fatigue is setting in. Take a short walk, stretch, or switch tasks for a few minutes. You’ll return with more clarity and a refreshed mind.
🔁 Erratic or inconsistent blinking?
This often signals a mix of stress and fatigue, especially during multitasking or emotionally demanding situations. Breathing exercises or a brief mindfulness session can help recalibrate your mental state.
Who Monitors Blink Rate Professionally?
In fields where focus and safety are critical, such as:
- Pilots
- Surgeons
- Truck drivers
- Athletes
- Air traffic controllers
Blink rate is often used as a non-invasive fatigue marker. Wearable tech and eye-tracking software can alert individuals when their blink patterns indicate declining performance—sometimes even before they consciously realize they’re tired.
As this technology becomes more accessible, it may play a larger role in everyday workplace ergonomics and mental wellness strategies.
Tips to Maintain Healthy Blinking and Reduce Mental Fatigue
- ✅ Take regular breaks
Follow a structured routine that includes mental rest every 60–90 minutes. - 💧 Hydrate
Dehydration can increase eye dryness and reduce concentration. - 💻 Adjust your screen settings
Reduce blue light and ensure proper brightness to minimize eye strain. - 👁️ Practice conscious blinking
Especially during screen-heavy tasks, blink slowly and intentionally to keep eyes moist and focused. - 🧘 Incorporate relaxation techniques
Breathwork, meditation, or short walks can help recalibrate your cognitive energy.
Final Thoughts
Your eyes don’t just help you see—they help you understand what’s going on inside your brain. The way you blink is more than a mechanical action; it’s a subtle, continuous indicator of mental fatigue, attention level, and neurological balance.
By learning to recognize changes in your eye blinking rate, you can spot early signs of cognitive overload, adjust your work habits, and prevent burnout before it sets in. It’s one of the body’s quietest, yet most reliable ways of saying: “Hey, it’s time to rest.”



